흐름장 추적
1. 흐름장 (flow field following)
흐름장은 공간의 각 지점에서 벡터를 정의하여 전체적인 흐름의 패턴을 나타냅니다. 자율 에이전트는 미리 정의된 벡터 흐름장과 상호작용하며 이동하게 되는데 흐름장의 벡터의 각 지점에서의 원하는 속도(desired)로 사용되며 각 위치에서 자율 에이전트의 조향력을 결정할 수 있습니다.
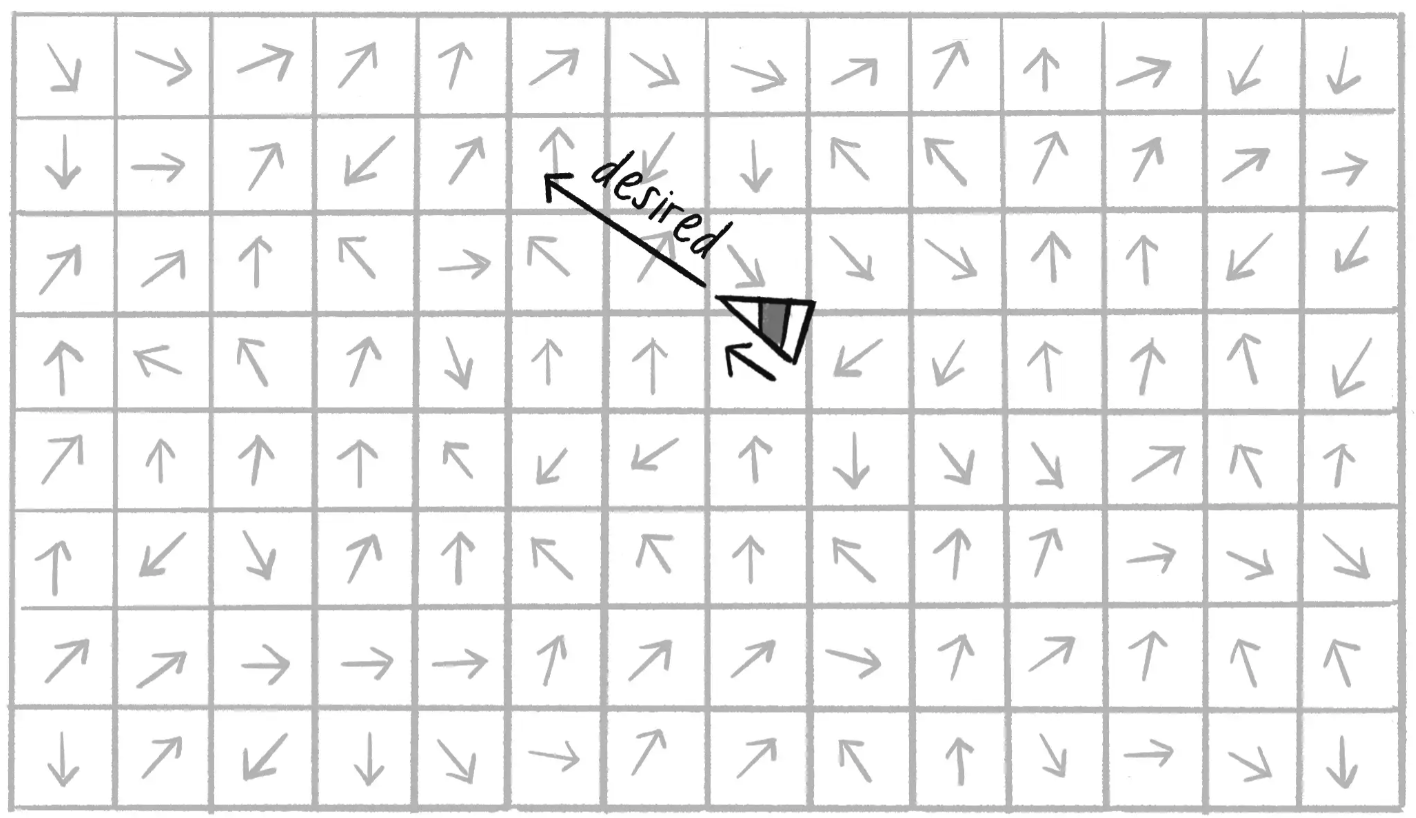
먼저 2차원 평면에서 흐름장을 만들어보도록 하겠습니다.
흐름장에서의 벡터를 ‘원하는 속도(desired)’로 설정하여 ‘조향력 = 원하는 속도 - 현재 속도’을 적용해 주면 자율 에이전트가 흐름장을 따라 이동하는 모습을 볼 수 있습니다. 이 때 Vehicle 클래스를 이용해 많은 vehicle 객체를 생성할 수 있습니다. 시뮬레이션을 클릭할 때 마다 변하는 흐름장의 벡터를 따라 자율 에이전트 객체들이 운동하는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
활동 1. 흐름장에서 운동하는 자율 에이전트
아래 p5.js 코드를 참고하면서 흐름장에서의 자율 에이전트의 움직임을 구현해 봅시다.
const resolution = 20;
let vehicles = [];
function setup() {
createCanvas(600, 400);
flowfield = new FlowField(resolution);
for (let i = 0; i < 120; i++) {
vehicles.push(
new Vehicle(random(width), random(height), random(2, 5), random(0.1, 0.5))
);
}
}
function draw() {
background(220);
flowfield.show();
for (let i = 0; i < vehicles.length; i++) {
vehicles[i].follow(flowfield);
vehicles[i].run();
}
}
class Vehicle {
constructor(x, y, ms, mf) {
this.position = createVector(x, y);
this.acceleration = createVector(0, 0);
this.velocity = createVector(0, 0);
this.r = 4;
this.maxspeed = ms;
this.maxforce = mf;
}
run() {
this.update();
this.edges();
this.show();
}
follow(flow) {
let desired = flow.lookup(this.position);
desired.mult(this.maxspeed);
let steer = p5.Vector.sub(desired, this.velocity);
steer.limit(this.maxforce);
this.applyForce(steer);
}
applyForce(force) {
this.acceleration.add(force);
}
update() {
this.velocity.add(this.acceleration);
this.velocity.limit(this.maxspeed);
this.position.add(this.velocity);
this.acceleration.mult(0);
}
edges() {
if (this.position.x < -this.r) this.position.x = width + this.r;
if (this.position.y < -this.r) this.position.y = height + this.r;
if (this.position.x > width + this.r) this.position.x = -this.r;
if (this.position.y > height + this.r) this.position.y = -this.r;
}
show() {
let theta = this.velocity.heading();
fill(127);
stroke(0);
strokeWeight(2);
push();
translate(this.position.x, this.position.y);
rotate(theta);
beginShape();
vertex(this.r * 2, 0);
vertex(-this.r * 2, -this.r);
vertex(-this.r * 2, this.r);
endShape(CLOSE);
pop();
}
}
class FlowField {
constructor(r) {
this.resolution = r;
this.cols = width / this.resolution;
this.rows = height / this.resolution;
this.field = new Array(this.cols);
for (let i = 0; i < this.cols; i++) {
this.field[i] = new Array(this.rows);
}
this.init();
}
init() {
noiseSeed(random(10000));
let xoff = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < this.cols; i++) {
let yoff = 0;
for (let j = 0; j < this.rows; j++) {
let angle = map(noise(xoff, yoff), 0, 1, 0, TWO_PI);
this.field[i][j] = p5.Vector.fromAngle(angle);
yoff += 0.1;
}
xoff += 0.1;
}
}
show() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.cols; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.rows; j++) {
stroke(255,0,0);
let w = width / this.cols;
let h = height / this.rows;
let v = this.field[i][j].copy();
v.setMag(w * 0.5);
let x = i * w + w / 2;
let y = j * h + h / 2;
strokeWeight(1);
line(x, y, x + v.x, y + v.y);
push();
translate(x + v.x, y + v.y);
rotate(v.heading());
line(0, 0, -5, -2);
line(0, 0, -5, 2);
pop();
}
}
}
lookup(position) {
let column = constrain(floor(position.x / this.resolution), 0, this.cols - 1);
let row = constrain(floor(position.y / this.resolution), 0, this.rows - 1);
return this.field[column][row].copy();
}
}